This is typically the outcome of the implementation of a new system or location for the data. The business driver is typically a migration or consolidation of applications in which new applications that share the same dataset are replaced or supplemented by legacy systems. Data migrations are often initiated these days as businesses switch from on-site infrastructure and apps to cloud-based storage and apps to simplify or transform their company. Until migration, data quality must be evaluated to ensure a safe implementation without data loss. The success rate of any data migration project depends directly on the data being transferred in terms of diversity, volume, and consistency.
As there are many small tasks involved in the process, such as assessing the storage capacity of the target database, testing applications, and maintaining data confidentiality, it needs careful preparation and testing.
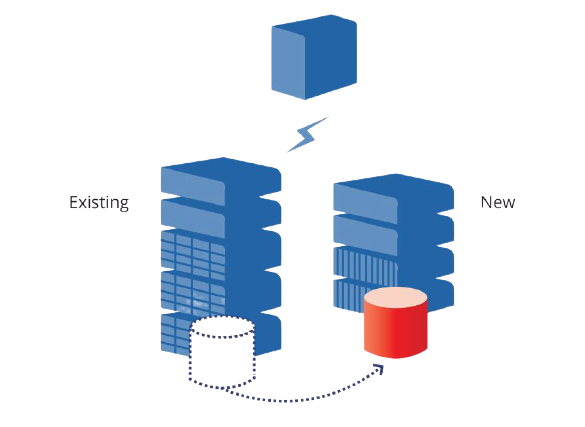
The process of moving data from existing arrays into more modern ones that allow access to it by other systems. Offers dramatically faster performance and more cost-effective scaling while allowing for functionality such as cloning, caching, and backup and disaster recovery to be expected data protection.
Moving to the cloud ensures scalability, requires fewer storage resources, and is cost-effective, making cloud migration one of the data management industry's latest trends. The complete or partial information properties, software, or services of an entity are deployed to the cloud in cloud migration. The firewall of the cloud protects the data being migrated.
When an company moves from one platform or vendor application to another, the application migration takes place. There is a special data model in and application. In addition, applications aren't portable. It may also mean replacing one application with a different one, such as switching from a different provider from one accounting software to a new accounting platform. Therefore, in the development and deployment environment, each application's operating systems, virtual machine configurations, and management tools can be different.

The strategy for data transfer is more than just transferring information from one repository to another. It requires several steps to perform a good transition and choose the correct migration method.
Choosing a strategy for data migration depends on the need for data migration. Is it that, after an acquisition or a merger, the company is consolidating processes or is it because of data overload? The foundation for the data migration strategy will be laid by solidifying the company goals. Alternatively, buying a code-free solution for data migration allows you the ability to conduct the transition at your convenience, speeds up the process, and reduces risks.
Analyzing business data is the next step in the data migration plan. With this assessment, answering the following questions will help:
Removing ROT data, compressing the remaining content, and translating enterprise-wide data into a single format are involved in this phase. For example, the transformation of information profiling is applied to a company's order data to analyze data available and delete duplicate / redundant records.
If the data has been profiled into a high-quality and functional form, the next step is to categorize it according to the criteria for migration. Categorization can be performed based on the type of product, ID, or some other criterion. It makes it easier for data to be routed into the correct buckets.
This phase requires evaluating the method of execution. Review the rules of the data and check if they work the way they are expected to, and map out any exceptions in your data flow. Even if the process is automated, it is best to keep a check on it to ensure that while implementing the process, you do not face any unforeseen problems.
In the data migration plan, this is the final stage in which everything falls into place. You will get well-organized and clean datasets from the above steps; all you have to do is move them from one system to ano If the data is migrated, a database or a data archive, such as a data mart or a data warehouse, may be a target system.